How do Self Driving Cars use AI
How do Self Driving Cars use AI
Self-driving cars are no longer just a futuristic dream. They’re now a real part of our world, transforming how we travel, work, and live. The question that sparks the most curiosity is: how do self driving cars use AI to think and make decisions like humans? The answer lies in a mix of Artificial Intelligence, sensors, and machine learning systems working together to sense, analyze, and act in real time.
From companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Google’s autonomous vehicle project, the world has already seen how far AI can push the boundaries of safe and smart driving. But to understand how this actually happens, we need to look at the brains behind the wheel — the AI systems that make it all possible.
The Role of AI in Autonomous Vehicles
Artificial Intelligence sits at the core of every self-driving system. It’s not just one technology — it’s a combination of several intelligent models that mimic how humans drive. The role of AI in autonomous vehicles is to process massive amounts of data from cameras, radars, LiDAR, and GPS sensors, helping the car see its surroundings just like human eyes and brains do.
AI algorithms analyze this data in milliseconds to detect pedestrians, road signs, obstacles, and even predict how nearby cars will move. This ability to sense and predict makes autonomous vehicles reliable and reduces the chances of human errors, the leading cause of road accidents worldwide.
A report by the World Health Organization revealed that 1.19 million people die every year due to road accidents. Self-driving cars, powered by AI, are being designed to lower these numbers drastically by removing human mistakes from driving decisions.

How AI Works in Self Driving Cars
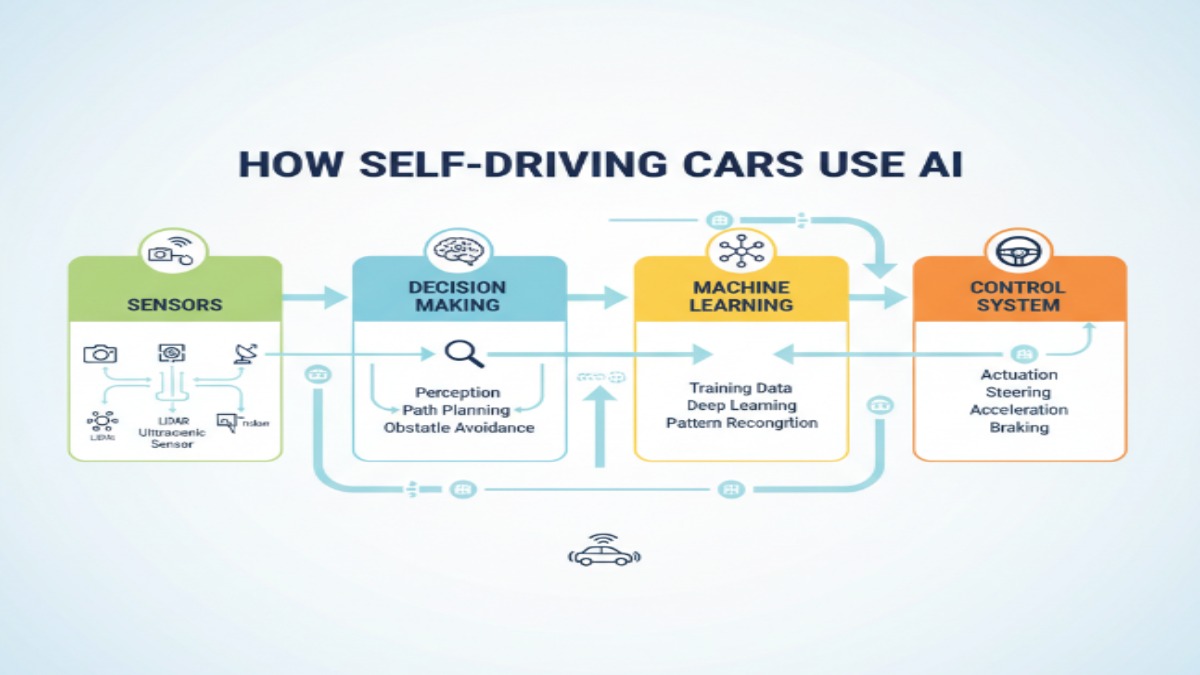
Understanding how AI works in self driving cars is like peeking inside the mind of a robotic driver. The AI system works through four main stages — perception, decision-making, planning, and control.
-
Perception: Cameras and LiDAR sensors create a 3D map of the environment. The AI processes these visuals to identify traffic lights, signs, vehicles, lanes, and pedestrians.
-
Decision-Making: The AI predicts how objects will move and decides what action the car should take next — such as slowing down, overtaking, or stopping.
-
Planning: Once a decision is made, the AI plans the safest path for the car to reach its destination.
-
Control: Finally, the AI sends commands to the car’s steering, brakes, and acceleration systems to execute the plan smoothly.
All these steps happen in fractions of a second — faster than a human could ever react.
AI Technology Behind Self Driving Cars
The AI technology behind self driving cars is built on advanced machine learning and deep learning models. These technologies help cars learn from millions of miles of real and simulated driving data. For example, Tesla’s Autopilot system learns from data collected by its global fleet of vehicles. Each car acts like a moving data sensor, sending information back to Tesla’s neural networks to improve future performance.
Waymo, another leader in autonomous driving, uses a deep neural network that processes over 1.2 million driving hours of training data. This massive data training helps AI predict situations that human drivers might miss, such as sudden lane changes or a cyclist turning unexpectedly.
For a deeper understanding of how AI systems process human-like decisions, you can read this helpful post on how AI understands human language — it breaks down the learning process behind intelligent machines in simple terms.
Artificial Intelligence in Self Driving Cars: The Core Components
The success of Artificial Intelligence in self driving cars depends on several key components working in harmony:
-
Sensor Fusion: AI collects and merges data from multiple sensors (LiDAR, radar, cameras) to create a single, detailed view of the environment.
-
Neural Networks: These are AI models inspired by the human brain, helping cars recognize patterns, such as traffic lights or road signs.
-
Path Planning: AI calculates the best route and continuously adjusts it based on real-time data.
-
Object Detection: Identifies cars, pedestrians, and obstacles to make instant driving decisions.
-
Control Algorithms: Translate AI’s decisions into physical movement — steering, acceleration, or braking.
This smart coordination is what allows cars like the Waymo One and Cruise Origin to operate safely even in crowded urban environments.
Real-World Examples of AI in Self Driving Cars
One of the best ways to understand how self driving cars use AI is to look at real-world examples. Over the last decade, several companies have tested and refined their autonomous driving systems across different cities and conditions.
Tesla Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD)
Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) systems are among the most recognized examples of AI technology behind self driving cars. Tesla cars use eight cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and radar to collect environmental data. This data feeds into Tesla’s neural networks, which process millions of driving scenarios every day.
Tesla’s AI doesn’t just learn from one car — it learns from all Teslas on the road. Every time a Tesla encounters a new driving situation, such as an unusual traffic sign or unexpected obstacle, the information is uploaded (anonymously) to Tesla’s data centers. The AI then updates its models to handle similar cases better in the future.
Elon Musk once explained that Tesla’s fleet had driven over 10 billion miles using Autopilot, and this massive amount of real-world data has helped the company’s AI continuously improve its perception and decision-making.
Waymo’s Driverless Taxis
Waymo, a Google subsidiary, is another great example of the role of AI in autonomous vehicles. Waymo’s self-driving taxis operate in cities like Phoenix and San Francisco without a human driver. The company’s AI system, called Waymo Driver, uses LiDAR, radar, and cameras to analyze surroundings in 360 degrees.
Waymo’s neural networks are trained on over 20 million miles of real-world driving and billions of miles in simulation. This massive data collection allows the AI to identify even rare driving events — such as a pedestrian suddenly crossing at night or a car door opening unexpectedly.
Uber ATG (Advanced Technologies Group)
Uber’s autonomous driving project, though sold to Aurora in 2020, made significant contributions to AI-based driving research. Uber ATG’s self-driving cars used deep learning models to predict how pedestrians and vehicles might move in complex intersections. Their tests in Pittsburgh and San Francisco offered key insights into real-time decision-making for AI-driven vehicles.
Experts’ Insights on Artificial Intelligence in Self Driving Cars
Experts in AI and automotive technology agree that while Artificial Intelligence in self driving cars has achieved incredible milestones, there’s still room for improvement.
Dr. Raquel Urtasun, former Chief Scientist at Uber ATG and now CEO of Waabi, believes that simulation plays a major role in AI training. According to her, “A car can’t learn from just driving on real roads — it needs millions of simulated scenarios to learn how to handle rare and dangerous situations safely.”
Similarly, Chris Urmson, co-founder of Aurora and one of the original leaders of Google’s self-driving project, emphasizes that “the key to safe autonomous driving isn’t just perception but prediction — understanding what other road users might do next.”
Both insights highlight the fact that AI works in self driving cars not just by reacting to what it sees but by predicting and planning ahead like an experienced human driver.
Challenges Faced by AI in Autonomous Vehicles
Even though AI has transformed driving, it still faces serious challenges before becoming a fully reliable driver. Some of these include:
1. Handling Unpredictable Human Behavior
AI struggles with interpreting human behavior on the road. For example, a pedestrian might make sudden movements or a driver might ignore a stop sign. Unlike humans, AI lacks emotional intuition, which makes predicting human mistakes harder.
2. Weather and Visibility Issues
AI systems depend heavily on sensors and cameras. During heavy rain, fog, or snow, visibility decreases, and sensor performance drops. This makes it difficult for the AI to maintain accurate perception and safe navigation.
3. Ethical Decision-Making
One of the most debated questions around how self driving cars use AI is ethical decision-making. If a crash becomes unavoidable, how should the car decide who to protect? This moral dilemma is known as the “trolley problem,” and it raises questions about how AI should prioritize human life.
4. Data Security and Privacy
AI systems collect massive amounts of driving data. Ensuring that this data remains secure is critical. Any hacking attempt could have serious consequences, especially if someone gains control of the car remotely.
You can read more about how to protect your privacy in the age of AI for insights on keeping your data safe in a world run by smart machines.
How AI Makes Self-Driving Cars Safer
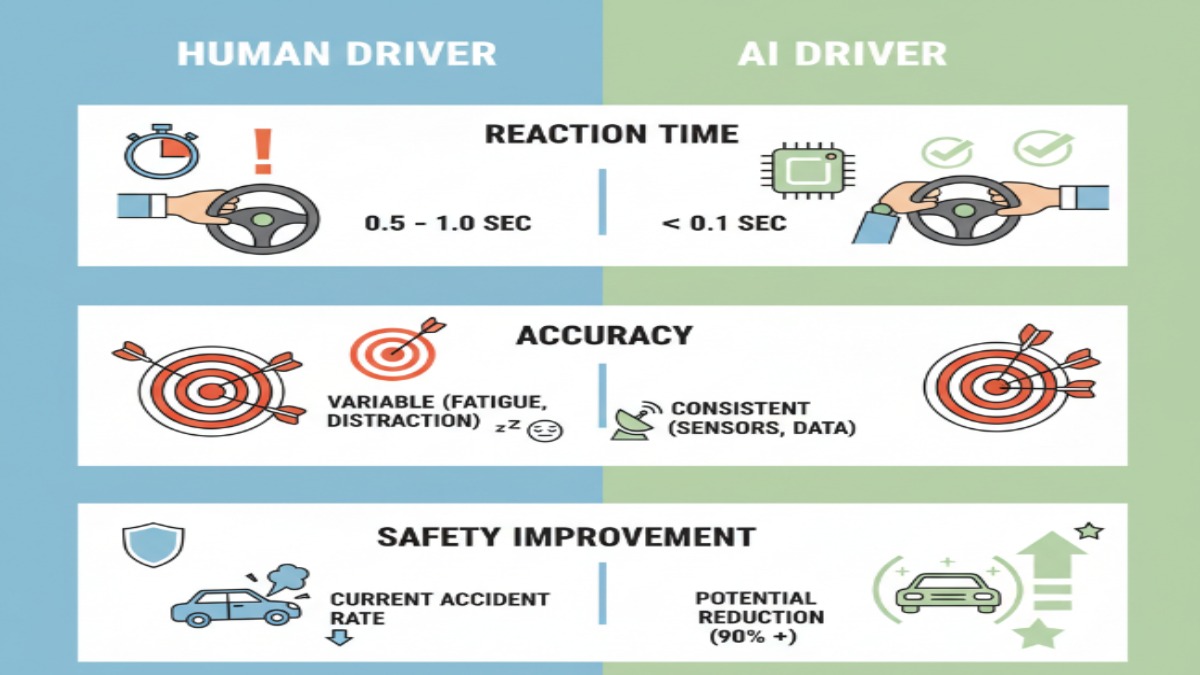
A study by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that human error contributes to 94% of all car accidents. By removing human limitations like fatigue, distraction, and slow reaction times, AI can drastically reduce crashes.
Here’s how AI improves safety:
-
Continuous Monitoring: AI never gets tired or distracted. It constantly scans the environment and reacts instantly.
-
Predictive Driving: Using deep learning, AI can predict other drivers’ behavior, reducing the chance of collisions.
-
Accident Prevention: AI’s decision-making is based purely on logic and data, not emotion.
-
Real-Time Updates: AI learns from new experiences and updates across the entire fleet.
This combination of consistency, speed, and learning makes AI-driven cars more reliable in many cases than human drivers.
AI and Human Collaboration: The Future of Driving
While full automation is the goal, experts believe the near future will be about collaboration between humans and AI. This approach, known as “human-in-the-loop” driving, allows humans to supervise while AI handles most driving tasks.
For instance, systems like Tesla Autopilot, GM Super Cruise, and Nissan ProPilot Assist use partial automation. The driver stays alert, while AI manages steering, acceleration, and braking. This partnership allows both the human brain and AI algorithms to complement each other, increasing safety and efficiency.
Future of Self Driving Cars with AI
The future of Artificial Intelligence in self driving cars looks promising. According to Statista, the autonomous vehicle market is expected to reach $2.3 trillion by 2030. This growth is driven by faster AI chips, better sensors, and advanced machine learning techniques.
Some upcoming trends include:
-
5G-Powered Vehicle Communication: Cars will talk to each other to share road and traffic information.
-
AI-Powered Traffic Systems: Cities will integrate AI with traffic lights and signals to manage flow more efficiently.
-
Enhanced Safety Protocols: AI will use predictive analytics to avoid accidents before they happen.
-
Sustainability: Electric self-driving cars will reduce emissions and improve energy efficiency.
As AI becomes smarter and more ethical, self-driving cars will become an everyday reality — not just a luxury technology.
How AI Learns to Drive: Training and Simulation
AI doesn’t learn to drive overnight. It undergoes thousands of hours of training using reinforcement learning — a process where the system improves through trial and error.
-
Simulation-Based Learning: Before real-world testing, AI systems drive in virtual environments that mimic complex traffic scenarios.
-
Sensor Feedback Loops: Every test drive helps refine object detection and path planning.
-
Continuous Improvement: The AI receives updates through cloud systems, learning from every car on the road.
A great example is Waymo’s “Carcraft” simulation system, which runs over 25,000 virtual cars at once, practicing over 20 million simulated miles every day. This constant learning keeps AI alert and adaptable.
AI in Self Driving Cars: Real Case Studies
Let’s look at two practical case studies that show how AI works in self driving cars in real-life conditions.
Case Study 1: Waymo vs. Human Driver
Waymo tested its autonomous taxis in Phoenix under various conditions — from bright sunlight to nighttime driving. After analyzing millions of miles, Waymo’s AI made 40% fewer safety-critical errors compared to human drivers. The car’s ability to react faster to unexpected events played a major role in preventing accidents.
Case Study 2: Tesla’s Autopilot Emergency Reaction
In 2021, a Tesla Model 3 in Norway detected a truck merging unexpectedly on a snowy road. Within milliseconds, the AI braked and changed lanes safely, avoiding a potential crash. The driver later shared that he wouldn’t have reacted as quickly. This incident proved that AI’s quick decision-making can save lives even in complex environments.
Ethical and Legal Questions Around AI in Driving
As self-driving cars become more common, questions arise about accountability. If an accident occurs, who is responsible — the car manufacturer, the software developer, or the owner?
Governments and organizations are still developing legal frameworks to address this. The European Union and the U.S. Department of Transportation are working on AI ethics guidelines to define liability and ensure transparency in autonomous decision-making.
Learning More About AI’s Broader Impact
To understand the bigger picture of AI’s role in technology and daily life, explore these in-depth reads:
These articles provide simple explanations and practical uses of AI across different areas of tech and productivity.
Conclusion
So, how do self driving cars use AI to drive themselves safely? They do it through a smart combination of sensors, neural networks, and machine learning models that mimic human thinking — but faster and more accurate.
From perception and decision-making to motion control and ethical reasoning, AI forms the backbone of every autonomous vehicle system. The role of AI in autonomous vehicles continues to evolve as companies collect more data, refine algorithms, and make cars smarter every day.
While full automation is still developing, there’s no doubt that Artificial Intelligence in self driving cars will shape the future of transportation, making our roads safer, cleaner, and more efficient than ever.
FAQS
What type of AI is used in self-driving cars?
Self-driving cars mainly use machine learning and deep learning algorithms. These help the system recognize objects, predict movements, and make safe driving decisions in real time.
Can AI completely replace human drivers?
Not yet. AI is advanced, but it still struggles with unpredictable human behavior and extreme weather conditions. For now, the best model is human-AI collaboration.
Are self-driving cars really safer than humans?
Yes, in most controlled environments. Studies show AI-driven systems can reduce accidents caused by fatigue, distraction, and human error — but safety still depends on data quality and regulatory standards.






